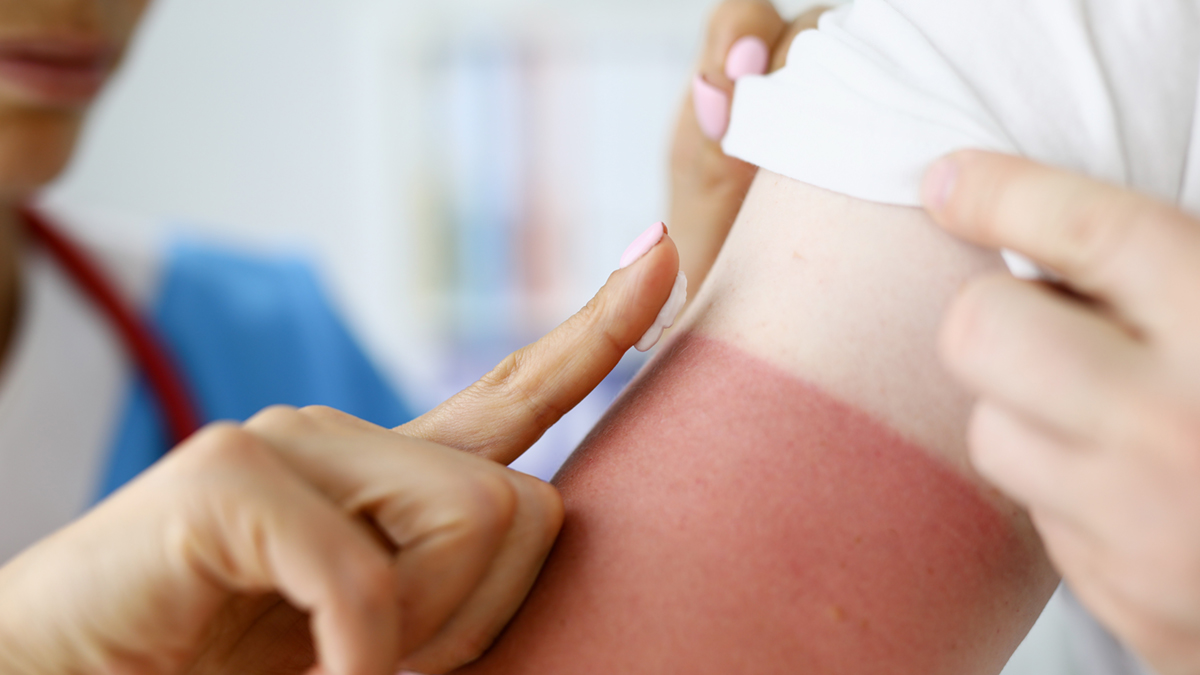
From winter snow activities to summers spent outside, damaging UV rays are a health hazard all year round. UV or ultraviolet rays describe the type of radiation present in sunlight. Exposure to UV rays can damage the skin, including premature aging, skin cancer, severe sunburns and sun poisoning, even on cloudy days.
As regions across the U.S. experience different climates that may exacerbate the risks of UV rays, Burn and Reconstructive Centers of America (BRCA) is raising awareness about the symptoms and dangers of sun poisoning in recognition of Poison Prevention Week (Mar. 20-26).
What is sun poisoning?
While referred to as “sun poisoning,” this condition is considered a severe reaction to prolonged or unprotected exposure to UV rays that may be characterized by severe sunburns or a rash. Everyone can be at risk of sun poisoning, though some conditions may increase these risks, such as:
- Fair skin
- Some medications like antibiotics, oral contraceptives and herbal supplements
- Skin cancer or a risk of skin cancer
- The beach where the sun may reflect off the sand and water
- Snowy places where the sun may reflect off the snow
- Some chemical peels and skin treatments
What are the symptoms of sun poisoning?
The symptoms of sun poisoning include those of a painful sunburn or rash plus:
- Blistering or peeling skin
- Skin that is red or painful
- Dehydration
- Fever
- Nausea or vomiting
- Dizziness or fainting
What are the risks of sun poisoning?
Sun poisoning can pose serious health complications if not treated right away. Dehydration is the number one concern when it comes to sun poisoning, along with infection, increased risk of skin cancer and severe sunburn.
How is sun poisoning treated?
Sun poisoning is treated in various ways depending on the symptoms and complications patients are experiencing. Patients may be given intravenous (IV) fluids to help recover from or prevent dehydration. If the skin is severely burned or a rash has formed, the doctor may prescribe steroid creams or oral steroids, pain medication or topical antibiotics to help relieve pain, prevent infection and supplement the body’s natural healing process.
Further Information
Sunburns and sun poisoning can be extremely dangerous, especially for those with more fragile skin, such as young children or older adults. It is important to take the proper precautions when spending the day outside. Whether it’s on ski slopes or at the beach, UV protection is important. To avoid severe sunburns or sun poisoning, consider:
- Limiting your time outdoors
- Wearing hats (especially important for young children)
- Bringing an umbrella
- Applying sunscreen of at least 35 SPF every 30 minutes
- Drinking a lot of water to stay hydrated
- Wearing UV protection gear such as long-sleeved shirts and sunglasses.
If you notice any of the symptoms listed above, please seek a medical professional immediately to get checked out and help prevent future complications. If you or any of your family members are at risk of skin cancer, make it a yearly goal to get a check-up by a dermatologist. These appointments can be lifesaving!
For more information, please visit us at www.burncenters.com or call us at (855) 863-9595.